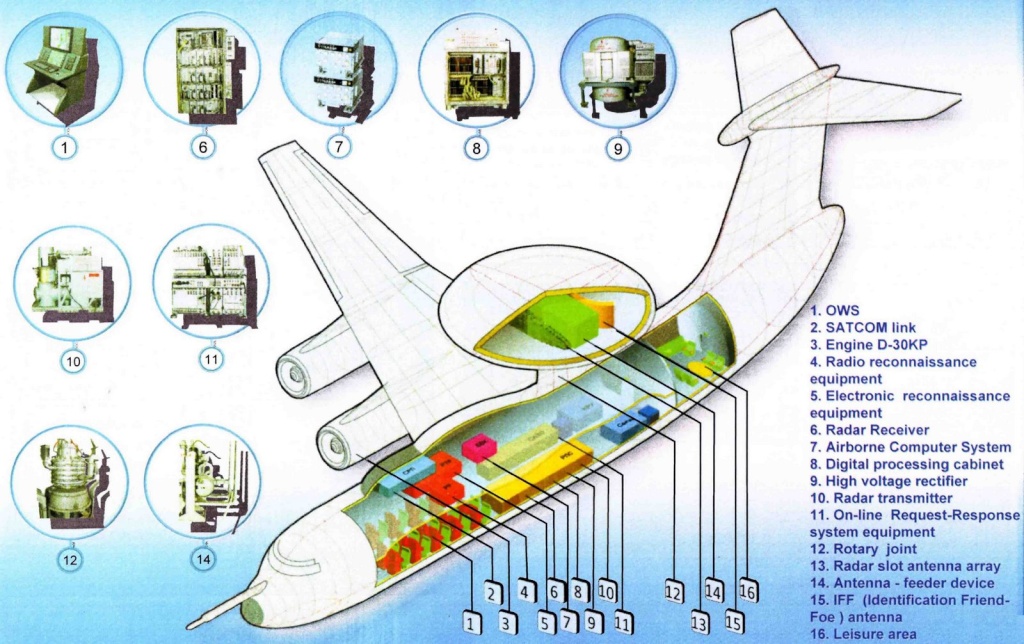
The Beriev A-50 (NATO reporting name "Mainstay") is a Soviet-built Airborne early warning and control (AEW) aircraft based on the Ilyushin Il-76 MD transport to replace the Tupolev Tu-126 'Moss'. The A-50 was developed and manufactured by the Beriev Aircraft Research and Engineering Complex Joint Stock Company based at Taganrog in the Rostov Region of Russia.
Beriev aircraft normally carry the Russian designation Be- followed by the number, however, the A-50 aircraft retained the well-known A-designation which Beriev allocated to the original prototype.
The A-50 aircraft detects and identifies airborne objects, determines their coordinates and flight path data and transfers the information to command posts. The A-50 also acts as a control centre, guiding fighter-interceptors and tactical air force aircraft to combat areas in order to attack ground targets at low altitudes. The role of the A-50 is comparable to that of the US's E-3 AEW system developed by Boeing.
A-50 Mainstay programme and development
The A-50 entered service with the Russian Air Force in 1984. Currently, 16 aircraft are operational in the Russian Air Force. The upgraded version, the A-50U was first announced in 1995 but did not enter testing until 2008. It then entered service in 2011. The upgraded A-50Us have extended the aircraft's the service life to 2020.
The modernised A-50 aircraft can now take more fuel on board with the same take-off weight, while increasing the range and mission time performance. A satellite navigation system integrated into flight and navigation complex offers a dramatic increase in the navigational accuracy.
Design
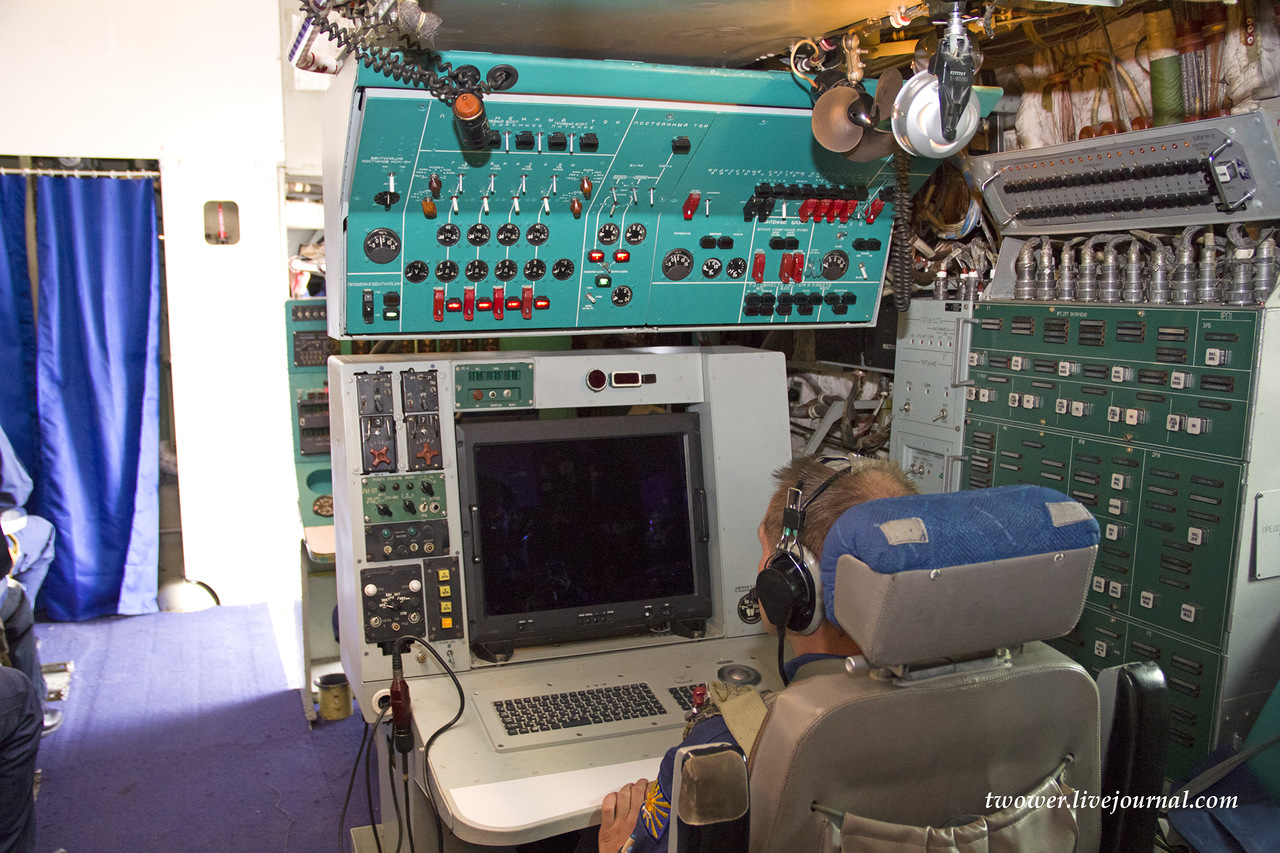
The A-50 is based on the Ilyushin Il-76 transport aircraft, but the majority of the modifications have been performed by Beriev. In comparison to the original airframe, the A-50 incorporates a lengthened fuselage with space for display consoles and communications sytems for the 10 mission specialists. A large rotating radome mounted is mounted above the fuselage. Installed in the forward portion of the radome is the antenna for the surveillance radar while the after section houses various data-link systems that allow the A-50 to vector up to 10 or 12 interceptors at once.
Avionics
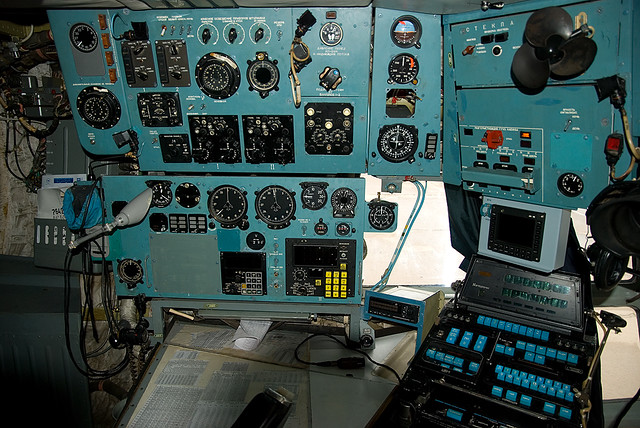
The A-50 AWACS is equipped with a flight control and navigation system used to ensure air navigation at all flight stages, in VFR and 1FR conditions, by day and night, in any season and in all latitudes. The system also provides flight control and navigation data intended for special systems. The aircraft's electronic equipment enables the crew to perform combat missions in a hostile ECM environment.
The A-50 AWACS is fitted with the NPK-T flight control and navigation system used to ensure air navigation during all flight stages in all-weather day and night and all-year operations performed at all geographical latitudes. The system also provides flight control and navigation data intended for mission specific systems and equipment.
Radar system
The A-50U airborne radar warning and guidance system is the Schnel-M produced by Vega. It comprises:
- radar station
- data reduction system
- interrogator-responder and signal transmission system
- digital computer complex
- identification friend or foe (IFF) equipment
- command radio link to guide fighters
- encoding communication system
- radio communication equipment
- telemetry / code equipment
- registering equipment.
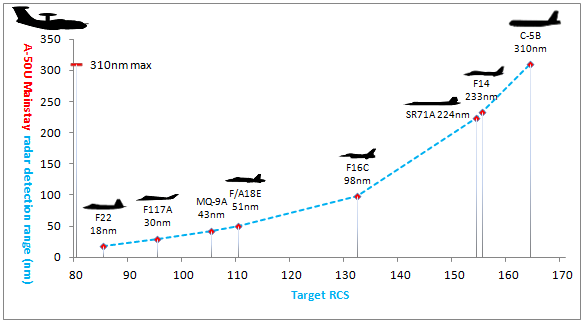
The radar and guidance systems have the capacity to track 50 to 60 targets simultaneously and to guide ten to 12 fighter aircraft simultaneously. The radar "Vega-M" is designed by MNIIP, Moscow, and produced by NPO Vega. The "Vega-M" is capable of tracking up to 50 targets simultaneously within 230 kilometers. Large targets, like surface ships, can be tracked at a distance of 400 km.
Countermeasures
The A-50 is fitted with a self-defence system when flying en-route and over patrol zones. The self-defence system ensures protection from guided and unguided weapons of the enemy's fighters attacking the aircraft from its front and rear hemispheres. The self-defence system includes an electronic countermeasures system.
The aircraft can also be protected from the enemy's fighter aircraft via guidance of friendly fighters.
The aircraft radio and electronics systems are robust against hostile jamming and provide good combat performance in dense electronic countermeasures environments.
Propulsion
The A-50 AWACS is motorized with four Soloviev D-30KP turbofan, 117,68 kN (26,500 lbf) each. The A-50 carries out patrol missions at an altitude of 5,000m to 10,000m. The patrol service ceiling is 10km. The maximum flight range of the aircraft is 5,000km and the flight endurance is seven hours 40 minutes. At a range of 2,000km, the A-50 can remain on patrol for up to one hour 25 minutes. The maximum take-off weight of the A-50 is 170,000kg. It can travel at a maximum speed of 800km/h. The aircraft can be refuelled by Il-78 tankers.
Variants
A-50M – Modernized Russian Version fitted with mid-air refueling capability.
A-50U – updated Russian variant
Izdeliye-676 – One-off stop-gap telemetry and tracking aircraft.
Izdeliye-776 – One-off stop-gap telemetry and tracking aircraft.
Izdeliye-976 (SKIP)] – (СКИП – Самолетный Контрольно-Измерительный Пункт, Airborne Check-Measure-and-Control Center) – Il-76 based Range Control and Missile tracking platform. Initially built to support Raduga Kh-55 cruise missile tests. Has fixed radar cover filled with other equipment and glassed navigator cockpit, (One prototype and five production conversions).
Izdeliye-1076 – One-off special mission aircraft with unknown duties.
A-50I – variant with an Israeli radar, designed for China but project cancelled under pressure of United States
A-50E/I – With Aviadvigatel PS-90 A-76 engines, with Israeli EL/W-2090 radar made for the Indian Air Force
Specifications
Type
AWACS airborne warning and control system
Engine
4 × Soloviev D-30KP turbofan, 117,68 kN (26,500 lbf) each
Altitude
5,000 - 10,000 m on patrol
Producer
Russia
Operators
Russia, India and Iran
Tracking detection
Simultaneously tracked targets: 50- 60
Simultaneously directed fighters: 10 - 12
Detection range: 220 -240 km
Speed
Maximum speed: 900 km/h (559 mph)
Range: 6,400 km (3,977 mi)
Service ceiling: 12,000 m (39,371 ft)
Take Off Weight
190,000 kg
Avionics
NPK-T flight control and navigation system, day and night flying system, self-defense electronic system
Dimension / Weight
Length: 49.59 m (152 ft 8 in)
Wingspan: 50.50 m (165 ft 6 in)
Height: 14.76 m (48 ft 5 in)
Wing area: 300 m² (3,228 ft²)
Empty weight: 75,000 kg (165,347 lb)