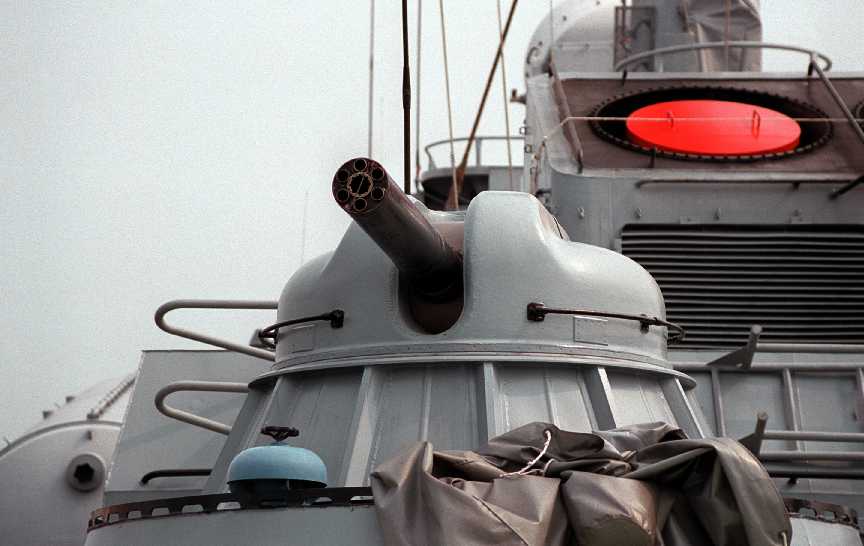
The AK-630 is a Soviet fully
automatic naval close-in weapon system based
on a six-barreled 30 mm Gatling gun.
In "630", "6" means 6 barrels and "30" means
30 mm. The AK-630 was one of the first ever CIWS systems: when it was
developed, there were no Phalanx,DARDO or Goalkeeper systems;
however, the long development time of the AK-630 partially negated this
advantage. Once operational, this weapon system was rapidly adopted, with up to
8 units installed in every new Soviet warship (from mine-hunters to aircraft
carriers), and hundreds produced in total.
Design of the AK_630 gun system startedin
1963. The first prototype was made in 1964 and trials were conducted until 1966. The trials of the
complete system with radar and controls went on untuil 1976 when the system was
accepted for service. Production started in 1969 in Tula, with a modified
AK-630M system accepted into service in 1979.
Specifications :
·
Gun: AO-18 six-barrel
30 mm Gatling gun.
·
Weight:
(Empty / with ammunition and control system)
· AK-630/630M:
1,850 kg (empty), 1,918 kg (with ammunition), 9,114 kg (with
ammunition and control systems)
·
AK-630M1-2:
2,500 kg (empty), 11,819 kg (with ammunition and control systems)
·
AK-306:
1,100 kg (empty), 1, 630 kg (with ammunition and control systems)
·
Elevation:
-12 to +88 degrees at 50 degree/s
·
Traverse:
±180 degrees at 70 degree/s
·
Muzzle
velocity:
900 m/s (MPDS round).
·
Rate of fire:
·
AK-630/630M:
83 round/s (5000 round/min).
·
AK-630M1-2:
166 round/s (10000 round/min).
·
Ammunition:
Fixed (HEI-FRAG, FRAG-T)
·
Ammunition
stowage:
A single below deck magazine
·
AK-630/630M:
2,000 rounds
·
AK-630M1-2:
4,000 rounds
·
AK-306:
500 rounds
·
Weapons range:
Effective range with HEI-FRAG (0.54 kg) shell, 4,000 m (4,375 yd)
·
Search and
track systems: A-213-Vympel-A, includes radar, optical, and TV control
systems
 |
| AK-630 M2 |