Yasen-class submarines were designed by the Malakhit Central Design Bureau, formed by the combination of SKB-143 and TsKB-16, with work on the initial design scheduled for start in 1977 and completion in 1985. Malakhit is one of the three Soviet/Russian submarine design centers, along with Rubin Design Bureau and Lazurit Central Design Bureau.
Yasen Class Submarine
Yasen-class submarines were designed by the Malakhit Central Design Bureau, formed by the combination of SKB-143 and TsKB-16, with work on the initial design scheduled for start in 1977 and completion in 1985. Malakhit is one of the three Soviet/Russian submarine design centers, along with Rubin Design Bureau and Lazurit Central Design Bureau.
Here goes the code of the element you want to show
SSBN Typhoon Class (Type 941), Russia
The Typhoon ballistic missile nuclear-powered (SSBN) submarines
are the largest submarines ever to be built. They were constructed at the
Severodvinsk Shipyard, on the White Sea near Archangel.
The first of the six members of the class to be commissioned was
TK 208 in 1981, followed by TK 202 in 1983, TK 12 in 1984, TK 13 in 1985, TK 17
in 1987 and TK 20 in 1989. The submarines were stationed with the Russian
Northern Fleet at Litsa Guba.
Of the six, only TK 17 and TK 20 are operational. TK 208 was
relaunched following refit in 2002 and is being used as a trials ship. TK 12
and TK 13 are decommissioned, waiting to be scrapped.
With assistance from the United States, through the cooperative
threat reduction programme, TK 202 has had its nuclear fuel removed by US
funded processing facilities and converted into forms suitable for long-term
storage or reuse. The UK has also agreed to take part in the dismantling of
Russia's decommissioned nuclear submarines.
Project 677 Lada Class / Project 1650 Amur Class Submarines, Russia
The Project 677 Lada Class diesel-electric submarines are being
built by Admiralty Shipyard for the Russian Navy. The class is also called the
Petersburg Class, after the lead submarine.
The Lada Class succeeds the Kilo Class submarines.
The keel for the lead sub in class, Sankt-Petersburg (B-585),
was laid down in December 1997 and launched in October 2004. The submarine was
delivered to the Russian Navy in April 2010 and commissioned in May 2010.
Two submarines under construction are: Kronshtadt (B-586) - laid
in July 2005 - and Sevastopol (B-587) - laid in November 2006. The Russian Navy
plans to build a total of eight Lada Class submarines.
MiG-35 / MiG-29M OVT / Fulcrum F
The Mikoyan MiG-35 (Fulcrum-F) is a 4++ generation fighter jet and a modification of the MiG-29M. It is equipped with air-to-air and air-to-surface guided missiles, as well as the Zhuk-A radar system. The MiG-29M OVT (Fulcrum F) highly maneuverable air superiority fighter was shown for the first time in August 2005 during the MAKS Air Show outside Moscow. The single-seat fighter, also marketed for export as the MiG-35, is powered by RD-33 OVT thrust vectoring control engines. The RD-33 OVT engines provide superior maneuverability capability to the aircraft enhancing its performance in close air-to-air engagements. The unique performance characteristics of this aircraft are based on RD-33 OVT thrust vectoring control engines.
Beriev A-50 Mainstay Airborne Early Warning and Control Aircraft (AEW&C)
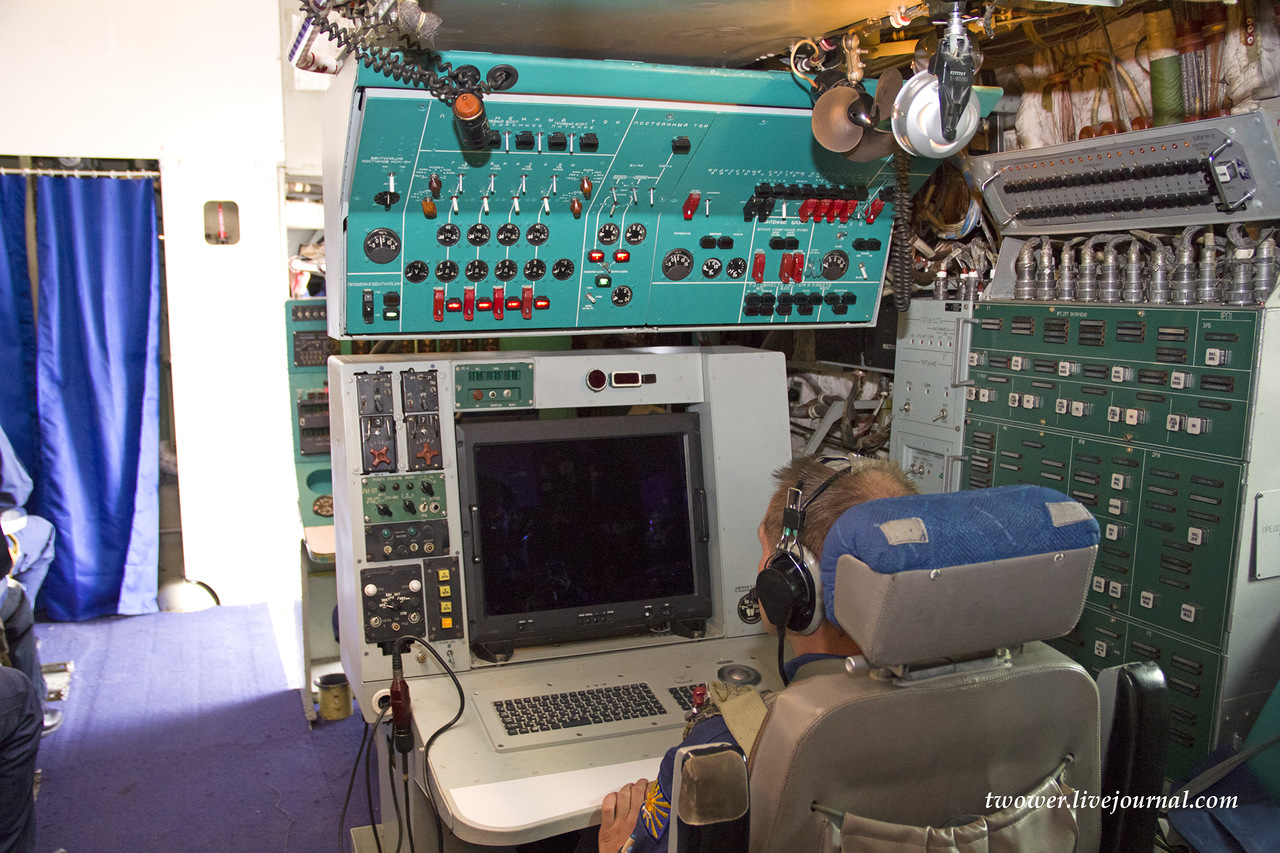
The Beriev A-50 (NATO reporting name "Mainstay") is a Soviet-built Airborne early warning and control (AEW) aircraft based on the Ilyushin Il-76 MD transport to replace the Tupolev Tu-126 'Moss'. The A-50 was developed and manufactured by the Beriev Aircraft Research and Engineering Complex Joint Stock Company based at Taganrog in the Rostov Region of Russia.
Beriev aircraft normally carry the Russian designation Be- followed by the number, however, the A-50 aircraft retained the well-known A-designation which Beriev allocated to the original prototype.
The A-50 aircraft detects and identifies airborne objects, determines their coordinates and flight path data and transfers the information to command posts. The A-50 also acts as a control centre, guiding fighter-interceptors and tactical air force aircraft to combat areas in order to attack ground targets at low altitudes. The role of the A-50 is comparable to that of the US's E-3 AEW system developed by Boeing.
A-50 Mainstay programme and development
The A-50 entered service with the Russian Air Force in 1984. Currently, 16 aircraft are operational in the Russian Air Force. The upgraded version, the A-50U was first announced in 1995 but did not enter testing until 2008. It then entered service in 2011. The upgraded A-50Us have extended the aircraft's the service life to 2020.
The modernised A-50 aircraft can now take more fuel on board with the same take-off weight, while increasing the range and mission time performance. A satellite navigation system integrated into flight and navigation complex offers a dramatic increase in the navigational accuracy.
Design
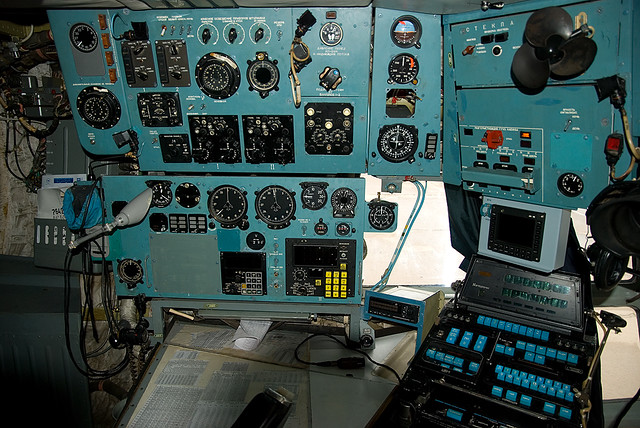
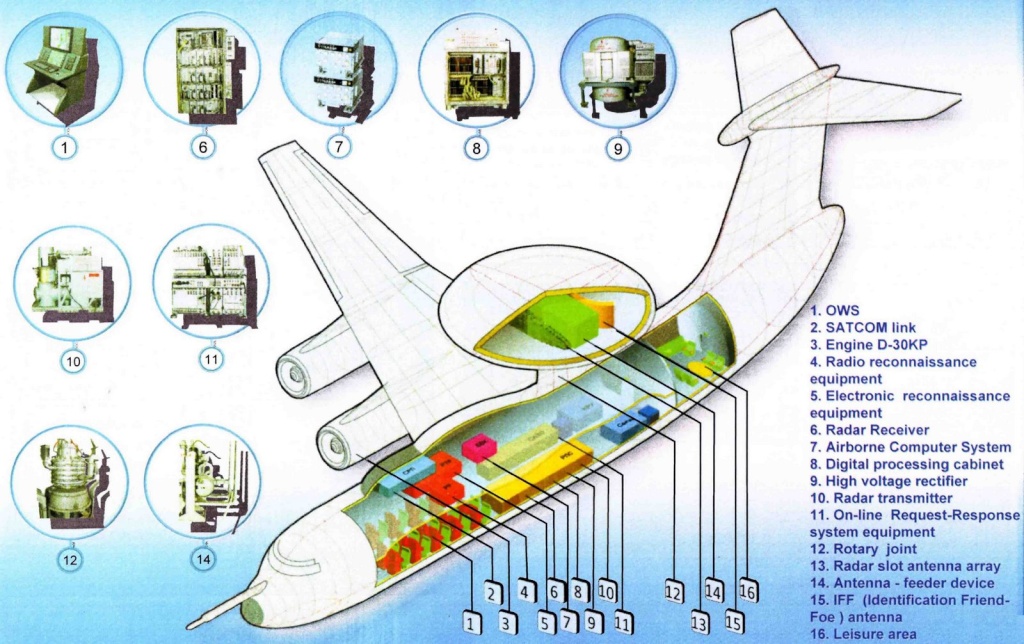
The A-50 is based on the Ilyushin Il-76 transport aircraft, but the majority of the modifications have been performed by Beriev. In comparison to the original airframe, the A-50 incorporates a lengthened fuselage with space for display consoles and communications sytems for the 10 mission specialists. A large rotating radome mounted is mounted above the fuselage. Installed in the forward portion of the radome is the antenna for the surveillance radar while the after section houses various data-link systems that allow the A-50 to vector up to 10 or 12 interceptors at once.
Avionics
The A-50 AWACS is equipped with a flight control and navigation system used to ensure air navigation at all flight stages, in VFR and 1FR conditions, by day and night, in any season and in all latitudes. The system also provides flight control and navigation data intended for special systems. The aircraft's electronic equipment enables the crew to perform combat missions in a hostile ECM environment.
The A-50 AWACS is fitted with the NPK-T flight control and navigation system used to ensure air navigation during all flight stages in all-weather day and night and all-year operations performed at all geographical latitudes. The system also provides flight control and navigation data intended for mission specific systems and equipment.
Radar system
The A-50U airborne radar warning and guidance system is the Schnel-M produced by Vega. It comprises:
- radar station
- data reduction system
- interrogator-responder and signal transmission system
- digital computer complex
- identification friend or foe (IFF) equipment
- command radio link to guide fighters
- encoding communication system
- radio communication equipment
- telemetry / code equipment
- registering equipment.
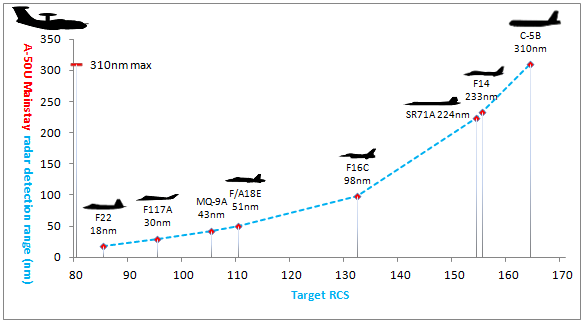
The radar and guidance systems have the capacity to track 50 to 60 targets simultaneously and to guide ten to 12 fighter aircraft simultaneously. The radar "Vega-M" is designed by MNIIP, Moscow, and produced by NPO Vega. The "Vega-M" is capable of tracking up to 50 targets simultaneously within 230 kilometers. Large targets, like surface ships, can be tracked at a distance of 400 km.
Countermeasures
The A-50 is fitted with a self-defence system when flying en-route and over patrol zones. The self-defence system ensures protection from guided and unguided weapons of the enemy's fighters attacking the aircraft from its front and rear hemispheres. The self-defence system includes an electronic countermeasures system.
The aircraft can also be protected from the enemy's fighter aircraft via guidance of friendly fighters.
The aircraft radio and electronics systems are robust against hostile jamming and provide good combat performance in dense electronic countermeasures environments.
Propulsion
The A-50 AWACS is motorized with four Soloviev D-30KP turbofan, 117,68 kN (26,500 lbf) each. The A-50 carries out patrol missions at an altitude of 5,000m to 10,000m. The patrol service ceiling is 10km. The maximum flight range of the aircraft is 5,000km and the flight endurance is seven hours 40 minutes. At a range of 2,000km, the A-50 can remain on patrol for up to one hour 25 minutes. The maximum take-off weight of the A-50 is 170,000kg. It can travel at a maximum speed of 800km/h. The aircraft can be refuelled by Il-78 tankers.
Variants
A-50M – Modernized Russian Version fitted with mid-air refueling capability.
A-50U – updated Russian variant
Izdeliye-676 – One-off stop-gap telemetry and tracking aircraft.
Izdeliye-776 – One-off stop-gap telemetry and tracking aircraft.
Izdeliye-976 (SKIP)] – (СКИП – Самолетный Контрольно-Измерительный Пункт, Airborne Check-Measure-and-Control Center) – Il-76 based Range Control and Missile tracking platform. Initially built to support Raduga Kh-55 cruise missile tests. Has fixed radar cover filled with other equipment and glassed navigator cockpit, (One prototype and five production conversions).
Izdeliye-1076 – One-off special mission aircraft with unknown duties.
A-50I – variant with an Israeli radar, designed for China but project cancelled under pressure of United States
A-50E/I – With Aviadvigatel PS-90 A-76 engines, with Israeli EL/W-2090 radar made for the Indian Air Force
Specifications
Type
AWACS airborne warning and control system
Engine
4 × Soloviev D-30KP turbofan, 117,68 kN (26,500 lbf) each
Altitude
5,000 - 10,000 m on patrol
Producer
Russia
Operators
Russia, India and Iran
Tracking detection
Simultaneously tracked targets: 50- 60
Simultaneously directed fighters: 10 - 12
Detection range: 220 -240 km
Speed
Maximum speed: 900 km/h (559 mph)
Range: 6,400 km (3,977 mi)
Service ceiling: 12,000 m (39,371 ft)
Take Off Weight
190,000 kg
Avionics
NPK-T flight control and navigation system, day and night flying system, self-defense electronic system
Dimension / Weight
Length: 49.59 m (152 ft 8 in)
Wingspan: 50.50 m (165 ft 6 in)
Height: 14.76 m (48 ft 5 in)
Wing area: 300 m² (3,228 ft²)
Empty weight: 75,000 kg (165,347 lb)
Spike Anti-Tank Missile
Rafael, based in Haifa, Israel,
manufactures the Spike family of anti-armour weapons. The weapons are
lightweight fire-and-forget anti-tank missiles and use electro-optical and
fibre-optic technologies. The systems are used by infantry soldiers, special rapid
reaction forces, ground forces and helicopter aircrew.
VC-25 - AIR FORCE ONE
Mission
The mission of the VC-25 aircraft -- Air Force One -- is to provide air transport for the president of the United States.
Features
The presidential air transport fleet consists of two specially configured Boeing 747-200B's -- tail numbers 28000 and 29000 -- with the Air Force designation VC-25. When the president is aboard either aircraft, or any Air Force aircraft, the radio call sign is "Air Force One."
The mission of the VC-25 aircraft -- Air Force One -- is to provide air transport for the president of the United States.
Features
The presidential air transport fleet consists of two specially configured Boeing 747-200B's -- tail numbers 28000 and 29000 -- with the Air Force designation VC-25. When the president is aboard either aircraft, or any Air Force aircraft, the radio call sign is "Air Force One."
MQ-1B PREDATOR
Mission
The MQ-1 Predator is an armed, multi-mission, medium-altitude, long endurance remotely piloted aircraft (RPA) that is employed primarily in a killer/scout role as an intelligence collection asset and secondarily against dynamic execution targets. Given its significant loiter time, wide-range sensors, multi-mode communications suite, and precision weapons -- it provides a unique capability to autonomously execute the kill chain (find, fix, track, target, engage, and assess) against high value, fleeting, and time sensitive targets (TSTs). Predators can also perform the following missions and tasks: intelligence, surveillance, reconnaissance (ISR), close air support (CAS), combat search and rescue (CSAR), precision strike, buddy-lase, convoy/raid overwatch, route clearance, target development, and terminal air guidance. The MQ-1's capabilities make it uniquely qualified to conduct irregular warfare operations in support of Combatant Commander objectives.
The MQ-1 Predator is an armed, multi-mission, medium-altitude, long endurance remotely piloted aircraft (RPA) that is employed primarily in a killer/scout role as an intelligence collection asset and secondarily against dynamic execution targets. Given its significant loiter time, wide-range sensors, multi-mode communications suite, and precision weapons -- it provides a unique capability to autonomously execute the kill chain (find, fix, track, target, engage, and assess) against high value, fleeting, and time sensitive targets (TSTs). Predators can also perform the following missions and tasks: intelligence, surveillance, reconnaissance (ISR), close air support (CAS), combat search and rescue (CSAR), precision strike, buddy-lase, convoy/raid overwatch, route clearance, target development, and terminal air guidance. The MQ-1's capabilities make it uniquely qualified to conduct irregular warfare operations in support of Combatant Commander objectives.
K-37M
The K-37M, RVV-BD or AA-13 Arrow western designation, is a long-range air-to-air missile being developed for the Mig-31BM interceptor. It has also had the names K-37, Izdeliye 610 and R-VD (Raketa-Vysokaya Dalnost, "Very Long Range Missile"), and the NATO codename 'Andi'.
It was designed to shoot down AWACS and other C4ISTAR aircraft whilst keeping the launch platform out of range of any fighters that might be protecting the target.
The K-37M seems to be a successor or leverage some technology from the R-37 air-to-air missile developed by the Soviet Union for the Mig-31M in the 1980s as a replacement for the R-33 missile. As of summer 2010 the missile system program was still in the development phase as the primary weapon for the Mig-31BM aircraft. The Russian reported that the K-37M underwent first firing testings in early 2012. The R-37M designation will apply when the new long-range air-to-air missile enters operational service with the Russian Air Force.
According to Defence Today the range depends on the flight profile, from 80 nautical miles (150 km) for a direct shot to 215 nautical miles (398 km) for a cruise glide profile. According to Jane's there are two variants, the R-37 and the R-37M; the latter has a jettisonable rocket booster that increases the range to "300-400km" (160–220 nm).
The missile was designed in the early 1980s and first flown in 1989. Testing of the R-37 continued through the 1990s; in 1994 a trial round scored a kill at a range of 162 nautical miles (300 km). However, the programme appears to have been dropped around 1998 on grounds of cost.
Work on the missile appears to have restarted in late 2006, as part of the MiG-31BM programme to update the Foxhound with a new radar and ground attack capability.
The Medium Extended Air Defense System (MEADS)
The Medium Extended Air Defense System (MEADS) is a tri-national missile defense project of the United States, Germany, and Italy. MEADS is currently in the design and development phase, but once operational, it will use the new Patriot Advanced Capability-3 (PAC-3) Missile Segment Enhancement missiles to protect ground forces and fixed military positions against attack from tactical ballistic missiles, low and high altitude cruise missiles, aircraft, and unmanned aerial vehicles.
Advanced Hypersonic Weapon (AHW), United States of America
The Advanced Hypersonic Weapon (AHW)
is a demonstrative long-range glide vehicle capable of flying within the
planet's atmosphere at hypersonic speed. The AHW technology demonstration
programme is managed by the US Army Space and Missile Defence Command (USASMDC)
/ Army Forces Strategic Command (ARSTRAT).
The technology was developed through
the cooperative effort of the US Department of Defence to evaluate a
conventional prompt global strike (CPGS) capability for striking time-sensitive
high-value targets.
In November 2011, AHW was launched
from the Pacific Missile Range Facility in Kauai, Hawaii, to the Reagan Test
Site on the Marshall Islands. The glide vehicle successfully hit the target,
which is located about 3,700km away from the launch site. The vehicle's flight
characteristics were gathered from space, air / sea and ground-based platforms.
The test was conducted to demonstrate
hypersonic boost-glide technologies and trial the capability for atmospheric
flight at long-ranges. The flight test was carried out in accordance with the
regulations of Strategic Arms Reduction Treaty I, as well as the
Intermediate-Range Nuclear Forces Treaty.
FN HERSTAL - Helicopter and Aircraft Weapon Systems
FN Herstal provides integrated airborne
weapon systems with unprecedented and unequalled firing capabilities for
multi-role helicopters and subsonic aircraft while maintaining simplicity of
use and crew safety.
Taking advantage of its century-long firearms
expertise, FN Herstal designs, develops and manufactures fully integrated
airborne weapon systems equipped with combat proven, single-barrel automatic
machine guns that offer reliability, accuracy, simplicity and safety.
FN Herstal's integrated airborne weapon
systems include crew-served or axially mounted machine guns, rocket launchers
and a complete range of ammunition.
More than just selling weapon systems, FN
Herstal develops the complete integration of the system together with the
helicopter manufacturer or directly with the end user. The company supervises
the installation of all its products and provides operator training as well as
a high-quality after-sales service to meet our customers' requirements.
For 120 years, FN Herstal has successfully
equipped generations of soldiers, airmen and marines. Its solid reputation can
be attributed to its rigorous professional ethics, ongoing effort to achieve
foremost quality, and commitment to efficient service and outstanding customer
support. Every weapon FN Herstal builds proudly bears the FN Herstal oval, a
mark that represents more than a century of experience making the finest
weapons in the world.
KIROV Class (Project 11442)
In
December 2011 it was reported that the Russian Defense Ministry was planning to
refit the Admiral Nakhimov, Admiral Lazarev and Admiral Ushakov missile
cruisers by 2020 in a major boost for the Russian Navy's combat strength. The
Admiral Ushakov, which has been docked at the Zvezdochka shipyard in
Severodvinsk, has not been determined.
Leopard 2 Main Battle Tank
The Leopard 2 is a main battle tank developed by Krauss-Maffei in the early 1970s for the West German Army. The tank first entered service in 1979 and succeeded the earlier Leopard 1 as the main battle tank of the German Army. Various versions have served in the armed forces of Germany and twelve other European countries, as well as several non-European nations. More than 3,480 Leopard 2s have been manufactured.
The Gryazev-Shipunov GSh-6-30
The Gryazev-Shipunov GSh-6-30 is a Russian 30mm cannon used by Soviet and later CIS military aircraft.
The GSh-6-30, designed in the early 1970s and entering
service in 1975, is a six barrelled Gatling gub similar in design to the
Gryazev-Shipunov GSh-6-23. It was based on the naval AQ-18 used in the AK-630
system. Unlike rotary cannon, it is gas operated rather than electric, aloowing
it to “ spin up “ to maximum rate of fire more quickly, allowing more rounds to
be placed on target in a short-duration burst. Ignition is electrical, as witj
the smaller GSh-6-23.
Trigat MR/Trigan
TRIGAT is a
third-generation anti-tank missile, being developed in two variations,
TRIGAT-MR for medium range applications and TRIGAT-LR for long range
applications. The missile is also known as PARS-3 (Panzerabewehr Rakensystem 3)
in Germany and AC 3G (AntiChar de 3e Generation) in France.
TRIGAT began as a
European programme involving France, Germany and the UK A Memorandum of
Understanding (MoU) was agreed by the governments of the three countries in
1988 to cover the development of TRIGAT. Belgium and the Netherlands joined as
associate members of the group in 1989. Trials of TRIGAT MR were completed in
July 1998.
AAI receives PBL contract for US Navy’s EA-6B, E2C and C-2 aircraft
The US Navy has
awarded a contract to AAI Logistics & Technical Services to deliver
performance base logistics (PBL) support for theEA-6B Prowler, E-2C Hawkeye and C-2 Greyhound aircraft.
Under the
contract, AAI will provide logistical services for 110 hydraulic components
that are used for the three aircraft.
Raytheon to equip GA-ASI's MQ-9 Reaper UAS with MALD
Raytheon has partnered with General Atomics
Aeronautical Systems (GA-ASI) to integrate its miniature air launched decoy
(MALD) into thePredator B/MQ-9 Reaper remotely piloted aircraft (RPA).
The companies have already completed the
ground verification test phase at GA-ASI's Gray Butte Flight Operations
Facility in Palmdale, California, US, in November 2012.
Raytheon Missile Systems Air Warfare Systems
vice president Harry Schulte said the new product offers enhanced electronic
warfare capability facilitating remote, unmanned suppression of enemy air
defences.
"Integrating MALD weaponry on remotely
piloted aircraft systems is integral to maintaining air superiority in today's
and tomorrow's conflicts," Schulte added.
Weighing less than 300lb, the ADM-160 MALD is
an advanced, air-launched and programmable flight vehicle designed to confuse
enemy integrated air defense systems (IADS), by duplicating friendly aircraft
flight profiles and radar signatures in the battlefield.
The low-cost vehicle is capable of
duplicating all combat flight profiles and signatures of US and allied aircraft
over a range of approximately 500nm, and executes a pre-programmed mission
following its release from the host aircraft, primarily the F-16
Fighting Falcon fighter aircraft.
MALD does not require communication with, or
guidance from, other aircraft or ground stations once it is launched.
As well as safeguarding valuable aircraft,
the system also offers counter-air operations to neutralise air defence systems
that pose a threat to the US and allied pilots. Incorporation of MALD into the
aircraft is expected to be completed in 2013.
The MQ-9 Reaper is a medium-to-high altitude,
long-endurance unmanned aircraft system (UAS) designed to conduct close air
support, air interdiction and intelligence, surveillance and reconnaissance
missions.
The drone is currently operational with the
US Air Force, Navy, Customs and Border Protection, as well as Italy and the UK
Royal Air Force (RAF).
Saab to modernise Swedish ground-based air defence system
The Swedish Defence Materiel
Administration (FMV) has awarded contracts to Saab to deliver and modernise the
national army's ground-based air defence systems.
Valued at a total Skr600m ($94.7m),
the two contracts cover an upgrade of existing units and supply of new systems
with ground-based air defence command, control and communication (C3) functions
based on its Giraffe agile multi-beam (AMB) multifunctional radar system.
Saab Electronic Defence Systems
business area head Micael Johansson said the contract further strengthens the
company's position in the field of ground-based air defence, both domestically
and worldwide.
THE ASTROS II MLRS
The ASTROS II
(Artillery SaTuration ROcket System) was developed by Avibras, which was
developing multiple launch rocket systems since the early 1960s. It
features modular design and employs rockets with calibers ranging from
127 mm to 300 mm. It was developed on the basis of a Tectran VBT-2028
6x6 all-terrain vehicle for enhanced mobility.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)