The KAI T-50 Golden Eagle,formerly known as the KTX-2, jet trainer and light attack aircraft is a family of South Korean supersonic advanced trainers and multirole light fighters, developed by Korea Aerospace Industries (KAI) with the American aerospace company Lockheed Martin. The T-50 is South Korea's first indigenous supersonic aircraft and one of the world's few supersonic trainers.
Development began in the late 1990s, and its maiden flight occurred in 2002. The aircraft entered active service with the Republic of Korea Air Force (ROKAF) in 2005.The aircraft was developed in the T-50A advanced trainer and T-50B lead in fighter trainer versions.
The T-50 LIFT is called the A-50 by the RoKAF. The T-50 is designed to provide pilot training for current and next-generation fighters such as advanced F-16s, F-22s and the F-35 joint strike fighter.
Origins
The T-50 program was originally intended to develop an indigenous trainer aircraft capable of supersonic flight, to train and prepare pilots for the KF-16 and F-15K, replacing trainers such as T-38 and A-37 that were then in service with the ROKAF.Prior South Korean aircraft programs include the turboprop KT-1 basic trainer produced by Daewoo Aerospace (now part of KAI), and license-manufactured KF-16.In general, the T-50 series of aircraft closely resembles the KF-16 in configuration.
The mother program, code-named KTX-2, began in 1992,but the Ministry of Finance and Economy suspended KTX-2 in 1995 due to financial constraints.The basic design of the aircraft was set by 1999.The development of the aircraft was funded 70% by the South Korean government, 17% by KAI, and 13% by Lockheed Martin.
The aircraft was formally designated as the T-50 Golden Eagle in February 2000.The T-50A designation was reserved by the U.S. military to prevent it from being inadvertently assigned to another aircraft model.Final assembly of the first T-50 took place between 15 January and 14 September 2001.The first flight of the T-50 took place in August 2002, and initial operational assessment from 28 July to 14 August 2003.
KAI and Lockheed Martin are currently pursuing a joint marketing program for the T-50 internationally. The ROKAF placed a production contract for 25 T-50s in December 2003, with aircraft scheduled to be delivered between 2005 and 2009.Original T-50 aircraft are equipped with the AN/APG-67(v)4 radar from Lockheed Martin.The T-50 is equipped with a GE F404 engine with Full Authority Digital Engine Control (FADEC) built under license by Samsung Techwin.Under the terms of the T-50/F404-102 co-production agreement, GE provides engine kits directly to Samsung Techwin who produces designated parts as well as performing final engine assembly and testing.
Improved versions
The program has expanded beyond a trainer concept to include the TA-50 light attack aircraft, as well as the FA-50 multirole fighter similar to the multirole KF-16. The TA-50 variant is a more heavily armed version of the T-50 trainer, intended for lead-in fighter training and light attack roles. It is equipped with the Elta EL/M-2032 fire control radar.The TA-50 is designed to operate as a full-fledged combat platform for precision-guided weapons, air-to-air missiles,and air-to-ground missiles.The TA-50 can mount additional utility pods for reconnaissance, targeting assistance, and electronic warfare. Reconnaissance and electronic warfare variants are also being developed, designated as RA-50 and EA-50.
The FA-50 is the most advanced version of the T-50, possessing more internal fuel capacity, enhanced avionics, a longer radome and a tactical datalink.It is equipped with a modified Israeli EL/M-2032 pulse-Doppler radar with Korean-specific modifications by LIG Nex1.The engine could be either Eurojet EJ200 or General Electric F414, upgraded to 20,000 lb or 22,000 lb thrust, roughly 12-25% higher than the F404's thrust and are offered to prospective customers for the T-50. The radar of the FA-50 has a range two-thirds greater than the TA-50's radar.The EL/M-2032 was initially chosen over Lockheed Martin's preferred AN/APG-67(V)4 and SELEX Vixen 500E active electronically scanned array (AESA) radars. Other AESA radars such as Raytheon Advanced Combat Radar and Northrop Grumman's Scalable Agile Beam Radar are options for future production and may be shared with the radar chosen for USAF and ROKAF F-16 fighters.Samsung Thales is also independently developing a domestic multi-mode AESA radar for the FA-50.
In December 2008, South Korea awarded a contract to KAI to convert four T-50s to FA-50 standard by 2012. In 2012, the ROKAF ordered 20 FA-50 fighters to be delivered by the end of 2014.The maiden flight of the FA-50 took place in 2011.60 FA-50 aircraft are to be produced for the ROKAF from 2013 to 2016.KAI received a 1.1 trillion won ($1 billion) order for FA-50 fighter aircraft in May 2013.
Overview
The T-50 Golden Eagle design is largely derived from the F-16 Fighting Falcon, and they have many similarities: use of a single engine, speed, size, cost, and the range of weapons.KAI's previous engineering experience in license-producing the KF-16 was a starting point for the development of the T-50.
The trainer has seating for two pilots in a tandem arrangement. The high-mounted canopy developed by Hankuk Fiber is applied with stretched acrylic, providing the pilots with good visibility, and has been tested to offer the canopy with ballistic protection against 4-lb objects impacting at 400 knots.The altitude limit is 14,600 metres (48,000 ft), and airframe is designed to last 8,000 hours of service.There are seven internal fuel tanks with capacity of 2,655 litres (701 US gal), five in the fuselage and two in the wings. An additional 1,710 litres (452 US gal) of fuel can be carried in the three external fuel tanks.T-50 trainer variants have a paint scheme of white and red, and aerobatic variants white, black, and yellow.
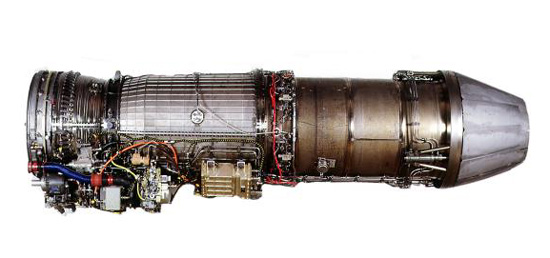
The T-50 uses a single General Electric F404-102 turbofan engine license-produced by Samsung Techwin,upgraded with a FADEC system jointly developed by General Electric and KAI.The engine consists of three-staged fans, seven axial stage arrangement, and an afterburner.The aircraft has a maximum speed of Mach 1.5.Its engine produces a maximum of 78.7 kN (17,700 lbf) of thrust with afterburner.The more powerful F414 and EJ200 engines have been suggested as the new engine for the T-50 family.
Avionics
The T-50's central processing unit and its operating system are developed by MDS Technology.The T-50's NEOS avionics operating system is the first and only real-time operating system to be developed by an Asian company, and holds both DO-178B and IEEE POSIX certification.Samsung Thales and LIG Nex1 are the main avionics and electronic warfare equipment developers for T-50 and its variants.Other South Korean companies and defense institutes such as DoDAAM Systems, Aeromaster, Intellics, and Korea Institute of Defense Analysis are responsible for the aircraft's secondary avionics and embedded systems, including store management computers,avionics testing equipment,flight data recorders,portable maintenance aids,data analysis software,post-flight data processing system,aircraft structure and engine management software,and mission planning and support systems.The TA-50 version is equipped with an ELTA EL/M-2032 fire control radar.
The T-50 is equipped with a Honeywell H-764G embedded global positioning/inertial navigation system and HG9550 radar altimeter.The aircraft is the first trainer to feature triple-redundant digital fly-by-wire controls.The cockpit panels, switches, and joysticks are produced by South Korea's FirsTec and Sungjin Techwin, head-up display by DoDaaM Systems, and multi-function display by Samsung Thales.Other South Korean subcontractors such as Elemech, Dawin Friction, and Withus cooperate in T-50 components production.Hanwha supplies the mechanical parts for the flight control system,and WIA supplies the undercarriage.
Armament and equipment
The TA-50 version mounts a three-barrel cannon version of the M61 Vulcan internally behind the cockpit, which fires linkless 20 mm ammunition.Wingtip rails can accommodate the AIM-9 Sidewinder missile, a variety of additional weapons can be mounted to underwing hardpoints.Compatible air-to-surface weapons include the AGM-65 Maverick missile, Hydra 70 and LOGIR rocket launchers, CBU-58 and Mk-20 cluster bombs, and Mk-82, −83, and −84 general purpose bombs.
FA-50 can be externally fitted with Rafael's Sky Shield or LIG Nex1's ALQ-200K ECM pods, Sniper or LITENING targeting pods, and Condor 2 reconnaissance pods to further improve the fighter's electronic warfare, reconnaissance, and targeting capabilities.Other improved weapon systems include SPICE multifunctional guidance kits,Textron CBU-97/105 Sensor Fuzed Weapon with WCMD tail kits, JDAM, JDAM-ER for more comprehensive air-to-ground operations, and AIM-120 missiles for BVR air-to-air operations.FA-50 has provisions for, but does not yet integrate, Python and Derby missiles, also produced by Rafael, and other anti-ship missiles, stand-off weapons, and sensors to be domestically developed by Korea.
Engines
The T-50 Golden Eagle is powered by a single General Electric turbofan engine, type F404-GE-102, with full authority digital electronic control (FADEC). It is a derivative of the 402 with additional improvements in the turbine and afterburner. The engine has twin side-mounted air intakes on either side of the fuselage under the wing.
The engine, with a three-fan stage and seven axial stage arrangement, is equipped with full authority digital engine control and generates 78.7kN with afterburn.
The aircraft has seven internal fuel tanks, five in the fuselage and two in the wings, which can carry 2,655l of fuel with the option of three additional 570l external fuel tanks.
The aircraft is fitted with an Argo-Tech fuel system. The power generator is supplied by Hamilton Sundstrand.
Landing gear
The aircraft is equipped with Messier Dowty retractable tricycle-type landing gear. Each unit is single wheeled and fitted with oleo pneumatic shock absorbers. The main wheels are retracted into the trunks of the engine air intakes. The nose wheel retracts forward.
T-50 performance
The T-50 can fly at a maximum speed of 1,837km per hour. The range and service ceiling of the aircraft are 1,851km and 16,764m respectively. The service life is 10,000 hours.
Variants
T-50: Advanced trainer version.
T-50I: Version of the T-50 for Indonesian Air Force.
T-50TH: Version of the T-50 for Royal Thai Air Force.
T-50B: Aerobatic specialized T-50 versionfor Korea Air Force's aerobatic display team, the Black Eagles.
TA-50: Lead-in fighter trainer and light attack version.
FA-50:[118] Multirole fighter all-weather version. Originally named A-50, a prototype from a converted T-50 first flew in 2011.
FA-50PH: Version of the FA-50 for Philippine Air Force.
T-50IQ: Version of the FA-50 for Iraqi Air Force.
Specifications
Data from Korea Aerospace,Lockheed Martin
General characteristics
Crew: 2
Length: 13.14 m (43.1 ft)
Wingspan: 9.45 m (31 ft) (with wingtip missiles)
Height: 4.94 m (16.2 ft)
Wing area: (23.69 m²)
Empty weight: 6,470 kg (14,285 lb)
Max takeoff weight: 12,300 kg (27,300 lb)
Powerplant: 1× General Electric F404 (built under license by Samsung Techwin[17]) afterburning turbofan
Dry thrust: 53.07 kN (11,925 lbf)
Thrust with afterburner: 78.7 kN (17,700 lbf)
Performance
Maximum speed: 1,640 km/h, 1,020 mph at 9,144 m or 30,000 ft (Mach 1.5
Range: 1,851 km (1,150 mi)
Service ceiling: 14,630 m (48,000 ft)
Rate of climb: 11,887 m/min (39,000 ft/min)
Thrust/weight: 0.96
Max g limit: -3 g / +8 g
Armament
Guns: 1× 20 mm (0.787 in) General Dynamics A-50 3-barrel rotary cannon
Hardpoints: Total of 7 with x4 underwing x2 wingtip and one under fuselage; holding up to 8,250 lb (3,740 kg) of payload
Rockets:
Hydra 70
LOGIR
Missiles:
Air-to-air:
AIM-9 Sidewinder
AIM-120 AMRAAM
Air-to-ground:
AGM-65 Maverick
Bombs:
Mk 82
Mk 83
CBU-97/105 Sensor Fuzed Weapon
Spice-equipped bombs
JDAM-equipped bombs
WCMD
Avionics
AN/APG-67 (T-50)
EL/M-2032 (TA-50 and FA-50)
Lockheed Martin Advanced Avionics
Note: armament for TA-50 and FA-50 only.